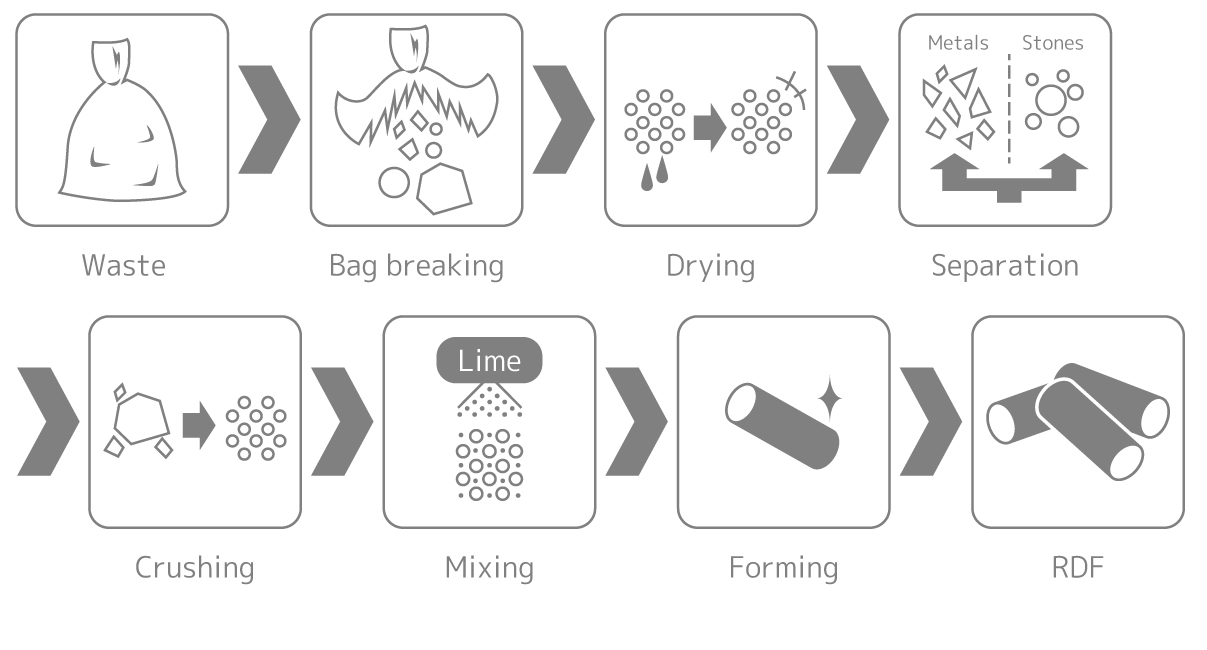
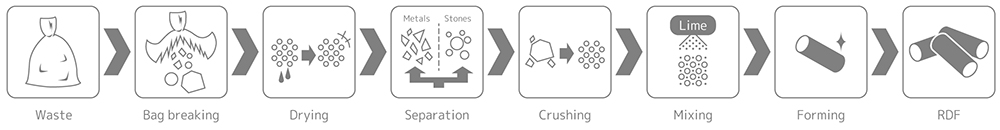
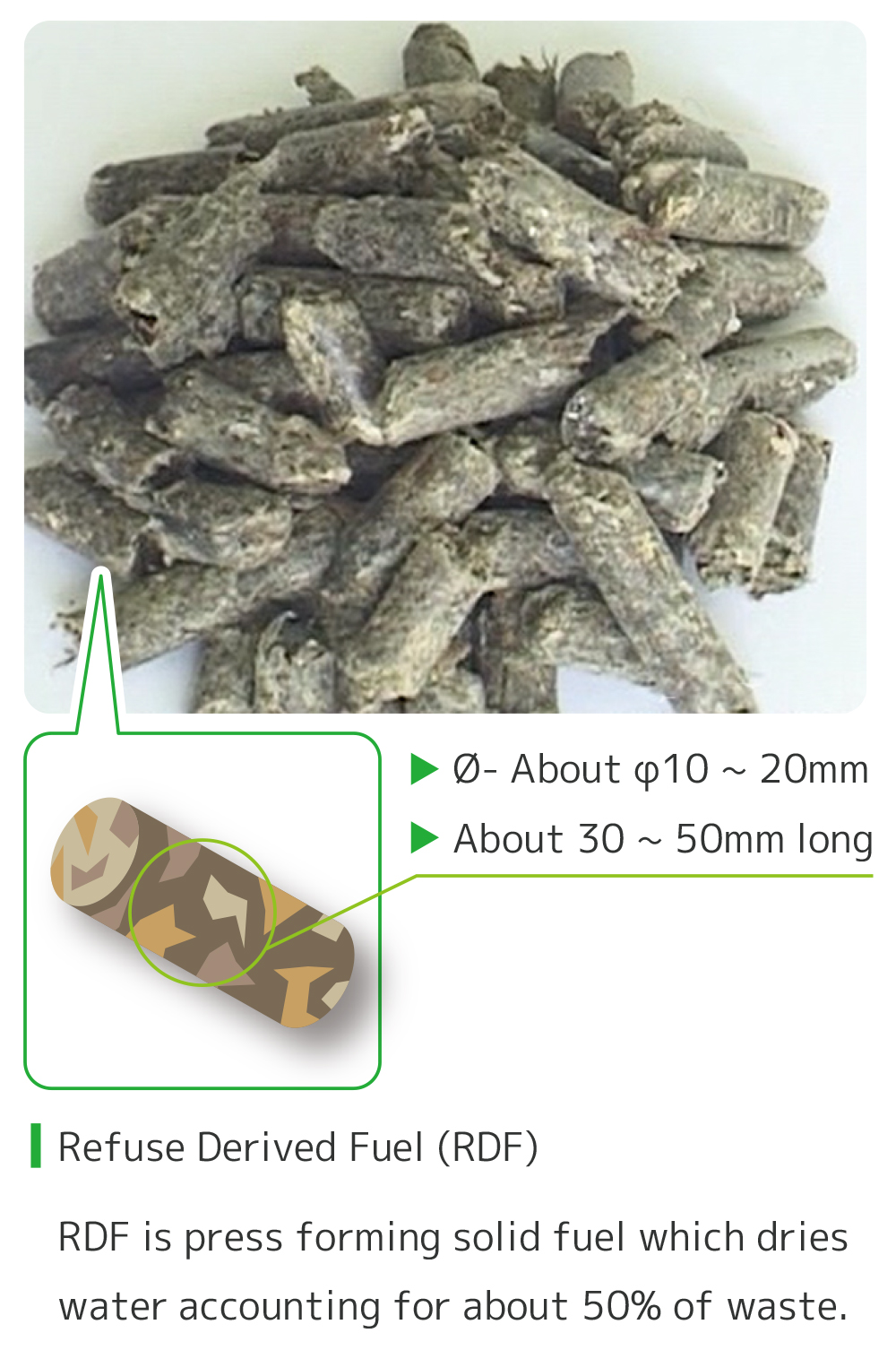
About 50% of combustible waste discharged by households, etc., consists of water. RDF means solid fuel with high calorific value, which is made of waste by decreasing moisture by drying and mixing lime, press forming and making solid in the shape of a crayon.
As RDF is dried and the volume is reduced with mixed lime, RDF offers an advantage that it does not emit offensive odors or corrode and can be transported and stored for long periods of time and handling is easier than ordinary combustible waste. In addition, as many metals and incombustibles are removed in the process of manufacturing RDF and moisture is reduced, it is possible to stably incinerate at higher temperatures than direct incineration of waste and efficient use of thermal energy and reductions in dioxins can be realized.


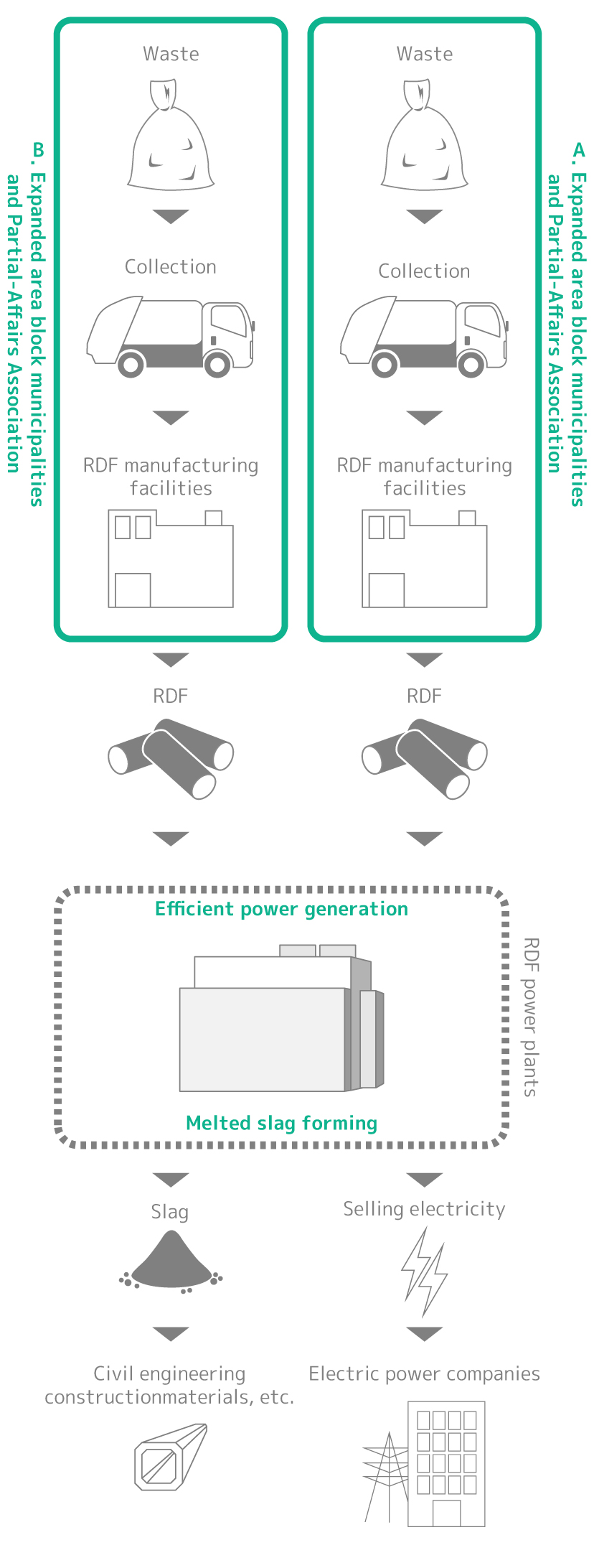
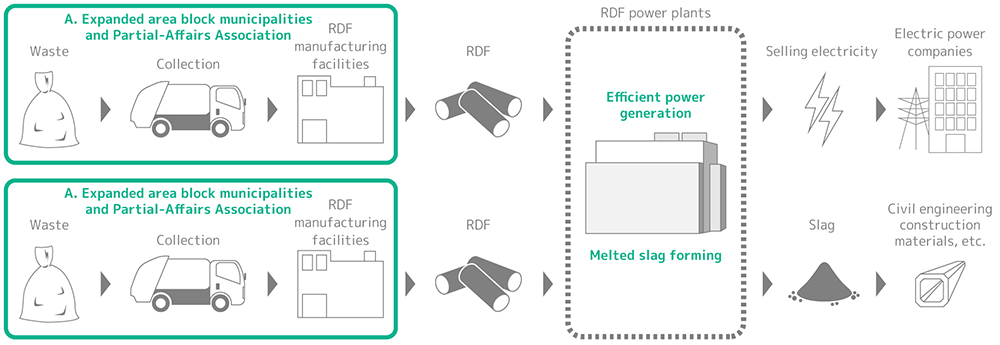
It is a process of recovery of thermal energy generated by incineration of RDF at high efficiency which generates power to reuse the energy for electric energy. As it is difficult to recover and use thermal energy at small-sized waste incineration facilities, it makes continuous incineration at high temperatures possible by collecting waste from expanded areas to make RDF, resulting in highly efficient power generation and reduction in carbon dioxide emissions and further reductions in environmental loads by dioxin, etc., through generation.